In the world of SEO, understanding the difference between XML Sitemap and HTML Sitemap is crucial for optimizing your website’s performance. These two types of sitemaps serve distinct purposes and play vital roles in enhancing search engine visibility. Let’s delve into their differences, benefits, and how they contribute to improving SEO. let’s dive in details of What’s the difference between XML Sitemap and HTML Sitemap
XML Sitemap and HTML Sitemap
XML Sitemap and HTML Sitemap are essential tools used by website owners to help search engines navigate and index their content efficiently. While both serve similar functions, they operate differently and cater to distinct aspects of website optimization.
Purpose and Functionality
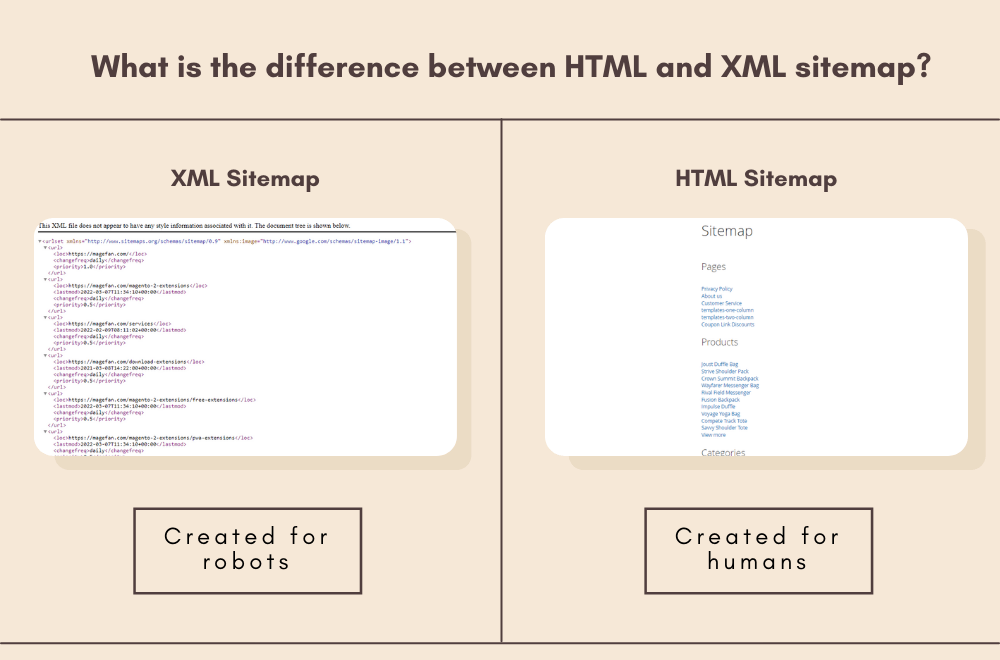
XML Sitemap
An XML Sitemap is a file that lists all the URLs of a website, along with additional information such as when each page was last updated, how often it changes, and its priority for crawling. This structured format helps search engines like Google understand the website’s structure and index its pages more intelligently.
An XML Sitemap is a crucial tool for website optimization, ensuring that search engines can efficiently crawl and index website content. It provides detailed information about each URL, such as its priority for crawling, frequency of updates, and the last time it was modified.
HTML Sitemap
On the other hand, an HTML Sitemap is designed for human visitors rather than search engines. It presents a hierarchical list of links to all the pages on a website, organized in a user-friendly format. HTML Sitemaps make navigation easier for users, especially on large websites with complex structures.
Key Differences Between XML Sitemap and HTML Sitemap
| Key Differences | XML Sitemap | HTML Sitemap |
| Purpose | Primarily for search engines to crawl and index content efficiently. | For human users to navigate the site easily. |
| Format | Uses XML format, which is machine-readable. | Uses HTML format for human readability. |
| Content | Includes additional metadata like last modified date, change frequency, and priority. | Focuses on displaying links and categories. |
| Accessibility | Typically hidden from website visitors and accessed by search engine crawlers. | Visible and accessible to users. |
| Visibility to Users | Not visible or accessible to users. | Visible and accessible to users. |
| Importance for SEO | Crucial for search engine optimization as it helps search engines understand the site structure and content hierarchy. | Helpful but not as critical for SEO as XML Sitemaps. |
| Frequency of Updates | Updated automatically by the website’s CMS or manually when changes are made. | Typically updated manually by webmasters. |
Benefits of Using XML Sitemap
- Facilitates faster indexing of new content by search engines.
- Helps in prioritizing important pages for crawling and indexing.
- Assists search engines in understanding the website’s structure and hierarchy.
- Improves the accuracy of search engine results by reducing crawl errors.
Benefits of Using HTML Sitemap
- Enhances user experience by providing a structured overview of the website’s content.
- Helps users find specific pages quickly, especially on large websites.
- Aids in improving website navigation and reducing bounce rates.
- Can contribute to increased user engagement and time spent on the site.
SEO Improvement
Both XML Sitemaps and HTML Sitemaps play a crucial role in improving SEO performance:
- XML Sitemaps ensure that search engines discover and index all relevant pages on the website, leading to better visibility in search results.
- HTML Sitemaps enhance user experience, which indirectly impacts SEO by reducing bounce rates and increasing user engagement metrics.

Best Practices for Creating and Using Sitemaps
XML Sitemap:
- Include all important pages and update the Sitemap regularly.
- Use relevant metadata such as last modified date and priority.
- Submit the XML Sitemap to search engines via Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools.
HTML Sitemap:
- Organize links logically and categorize them for easy navigation.
- Keep the HTML Sitemap updated as new pages are added or removed.
- Ensure the HTML Sitemap is accessible from the website’s footer or main navigation menu.
Maintenance
Regular updates and maintenance of both XML and HTML Sitemaps are essential for optimal performance. This includes adding new pages, removing outdated content, and updating metadata as needed. Keeping Sitemaps up-to-date ensures that search engines and users can navigate the website effectively.
Adding New Pages:
Regularly adding new pages to your XML and HTML Sitemaps is crucial for keeping search engines updated about your website’s content. This includes adding new blog posts, product pages, service pages, or any other relevant content that you publish on your site. By adding new pages to your Sitemaps, you help search engines discover and index this fresh content more efficiently.
Removing Outdated Content:
Over time, some of your website content may become outdated or irrelevant. It’s important to review your XML and HTML Sitemaps periodically and remove any outdated pages or content that no longer serve a purpose. This not only keeps your Sitemaps clean and organized but also prevents search engines from indexing irrelevant content that could affect your site’s ranking.
Updating Metadata:
Metadata, including titles, descriptions, and keywords, plays a significant role in how search engines understand and display your website in search results. Regularly updating metadata in your XML and HTML Sitemaps ensures that search engines have accurate and relevant information about your pages. This includes optimizing metadata for SEO by using relevant keywords, compelling descriptions, and clear titles that accurately reflect the content of each page.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between XML Sitemap and HTML Sitemap is key to implementing a comprehensive SEO strategy. While XML Sitemaps focus on search engine optimization by providing structured data for crawling and indexing, HTML Sitemaps enhance user experience by simplifying navigation. Incorporating both types of Sitemaps can lead to improved search engine visibility and user engagement.
Readmore : What is Robots txt and how to implement it WordPress and non-WordPress sites
FAQ’s
An XML Sitemap helps search engines crawl and index a website’s content more efficiently.
It’s recommended to have both for optimal SEO and user experience.
Update your XML Sitemap whenever there are significant changes to your website’s content or structure.
While HTML Sitemaps don’t directly impact SEO rankings, they contribute to better user experience, which indirectly affects SEO metrics.


